Abstract
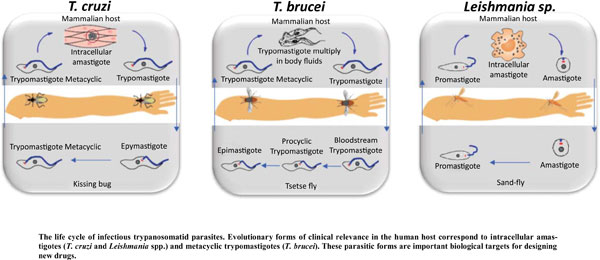
Trypanosomatidae family belongs to the Kinetoplastida order, which consists of obligatory parasites that affect plants and all classes of vertebrates, especially humans and insects. Among the heteroxenic parasites, Leishmania spp., Trypanosoma cruzi, and T. brucei are protozoa of most significant interest for medicinal chemistry, being etiological agents of Leishmaniasis, Chagas, and Sleep Sickness diseases, respectively. Currently, inefficient pharmacotherapy, especially in chronic phases and low selectivity towards parasite/host cells, justifies the need to discover new drugs to treat them effectively. Among other targets, the sterol 14α-demethylase (CYP51), an enzyme responsible for ergosterol's biosynthesis in Trypanosomatidae parasites, has received more attention in the development of new bioactive compounds. In this context, antifungal ravuconazole proved to be the most promising drug among this class against T. cruzi, being used in combined therapy with Bnz in clinic trials. Non-antifungal inhibitors, such as VFV and VNF, have shown promising results against T. cruzi and T.brucei, respectively, being tested in Bnz-combined therapies. Among the experimental studies involving azoles, compound (15) was found to be the most promising derivative, displaying an IC50 value of 0.002 μM against amastigotes from T. cruzi, in addition to being non-toxic and highly selective towards TcCYP51 (< 25 nM). Interestingly, imidazole analog (16) was active against infectious forms of these three parasites, demonstrating Ki values of 0.17, 0.02, and 0.36 nM for CYP51 from T. cruzi, T. brucei, and L. infantum. Finally, this review will address promising inhibitors targeting sterol 14α-demethylase (CYP51) from Trypanosomatidae parasites, highlighting SAR studies, interactions with this target, and recent contributions and advances in the field, as well.
Keywords: Drug discovery, Sterol 14α-demethylase, Trypanosomatidae, Leishmaniasis, HAT, Trypanosomiasis.
Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry
Title:Sterol 14α-Demethylase from Trypanosomatidae Parasites as a Promising Target for Designing New Antiparasitic Agents
Volume: 21 Issue: 21
Author(s): Paulo Fernando da Silva Santos-Júnior, Martine Schmitt, João Xavier de Araújo-Júnior and Edeildo Ferreira da Silva-Júnior*
Affiliation:
- Chemistry and Biotechnology Institute, Federal University of Alagoas, Campus A.C. Simões, Lourival Melo Mota Avenue, Maceió57072-970,Brazil
Keywords: Drug discovery, Sterol 14α-demethylase, Trypanosomatidae, Leishmaniasis, HAT, Trypanosomiasis.
Abstract: Trypanosomatidae family belongs to the Kinetoplastida order, which consists of obligatory parasites that affect plants and all classes of vertebrates, especially humans and insects. Among the heteroxenic parasites, Leishmania spp., Trypanosoma cruzi, and T. brucei are protozoa of most significant interest for medicinal chemistry, being etiological agents of Leishmaniasis, Chagas, and Sleep Sickness diseases, respectively. Currently, inefficient pharmacotherapy, especially in chronic phases and low selectivity towards parasite/host cells, justifies the need to discover new drugs to treat them effectively. Among other targets, the sterol 14α-demethylase (CYP51), an enzyme responsible for ergosterol's biosynthesis in Trypanosomatidae parasites, has received more attention in the development of new bioactive compounds. In this context, antifungal ravuconazole proved to be the most promising drug among this class against T. cruzi, being used in combined therapy with Bnz in clinic trials. Non-antifungal inhibitors, such as VFV and VNF, have shown promising results against T. cruzi and T.brucei, respectively, being tested in Bnz-combined therapies. Among the experimental studies involving azoles, compound (15) was found to be the most promising derivative, displaying an IC50 value of 0.002 μM against amastigotes from T. cruzi, in addition to being non-toxic and highly selective towards TcCYP51 (< 25 nM). Interestingly, imidazole analog (16) was active against infectious forms of these three parasites, demonstrating Ki values of 0.17, 0.02, and 0.36 nM for CYP51 from T. cruzi, T. brucei, and L. infantum. Finally, this review will address promising inhibitors targeting sterol 14α-demethylase (CYP51) from Trypanosomatidae parasites, highlighting SAR studies, interactions with this target, and recent contributions and advances in the field, as well.
Export Options
About this article
Cite this article as:
da Silva Santos-Júnior Fernando Paulo , Schmitt Martine , de Araújo-Júnior Xavier João and da Silva-Júnior Ferreira Edeildo*, Sterol 14α-Demethylase from Trypanosomatidae Parasites as a Promising Target for Designing New Antiparasitic Agents, Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry 2021; 21 (21) . https://dx.doi.org/10.2174/1568026621666210303144448
| DOI https://dx.doi.org/10.2174/1568026621666210303144448 |
Print ISSN 1568-0266 |
| Publisher Name Bentham Science Publisher |
Online ISSN 1873-4294 |
Call for Papers in Thematic Issues
Chemistry Based on Natural Products for Therapeutic Purposes
The development of new pharmaceuticals for a wide range of medical conditions has long relied on the identification of promising natural products (NPs). There are over sixty percent of cancer, infectious illness, and CNS disease medications that include an NP pharmacophore, according to the Food and Drug Administration. Since NP ...read more
Current Trends in Drug Discovery Based on Artificial Intelligence and Computer-Aided Drug Design
Drug development discovery has faced several challenges over the years. In fact, the evolution of classical approaches to modern methods using computational methods, or Computer-Aided Drug Design (CADD), has shown promising and essential results in any drug discovery campaign. Among these methods, molecular docking is one of the most notable ...read more
Drug Discovery in the Age of Artificial Intelligence
In the age of artificial intelligence (AI), we have witnessed a significant boom in AI techniques for drug discovery. AI techniques are increasingly integrated and accelerating the drug discovery process. These developments have not only attracted the attention of academia and industry but also raised important questions regarding the selection ...read more
From Biodiversity to Chemical Diversity: Focus of Flavonoids
Flavonoids are the largest group of polyphenols, plant secondary metabolites arising from the essential aromatic amino acid phenylalanine (or more rarely from tyrosine) via the phenylpropanoid pathway. The flavan nucleus is the basic 15-carbon skeleton of flavonoids (C6-C3-C6), which consists of two phenyl rings (A and B) and a heterocyclic ...read more
 39
39
- Author Guidelines
- Graphical Abstracts
- Fabricating and Stating False Information
- Research Misconduct
- Post Publication Discussions and Corrections
- Publishing Ethics and Rectitude
- Increase Visibility of Your Article
- Archiving Policies
- Peer Review Workflow
- Order Your Article Before Print
- Promote Your Article
- Manuscript Transfer Facility
- Editorial Policies
- Allegations from Whistleblowers
- Announcements
Related Articles
-
Cardiovascular disease management through restrained inflammatory responses
Current Pharmaceutical Design Functions of S100 Proteins
Current Molecular Medicine Mediterranean Diet, Brain and Muscle: Olive Polyphenols and Resveratrol Protection in Neurodegenerative and Neuromuscular Disorders
Current Medicinal Chemistry Editorial [ Hot Topic: Modifying Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Novel Cardiovascular Targets for Treatment by Noninvasive Imaging Techniques (Executive Editors: Aurelio Leone and Luigi Landini) ]
Current Pharmaceutical Design Stem Cells in Cardiovascular Regeneration: From Preservation of Endogenous Repair to Future Cardiovascular Therapies
Current Pharmaceutical Design Expression of microRNAs (133b and 138) and Correlation with Echocardiographic Parameters in Patients with Alcoholic Cardiomyopathy
MicroRNA Novel approaches to examine the regulation of voltage-gated calcium channels in the heart
Current Molecular Pharmacology Targeting microRNAs in Pathological Hypertrophy and Cardiac Failure
Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry Genes and Hypertension
Current Pharmaceutical Design Mitochondrial, Metabolic and Genotoxic Effects of Antiretroviral Nucleoside Reverse-Transcriptase Inhibitors
Anti-Infective Agents in Medicinal Chemistry Therapeutic Interventions for Advanced Glycation-End Products and its Receptor- Mediated Cardiovascular Disease
Current Pharmaceutical Design L-Carnitine - Metabolic Functions and Meaning in Humans Life
Current Drug Metabolism TGR5 as a Therapeutic Target for Treating Obesity
Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry Diabetic Cardiovascular Disease – AMP-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) as a Therapeutic Target
Cardiovascular & Hematological Agents in Medicinal Chemistry Red Cell Distribution Width: A Routinely Available Biomarker with Important Clinical Implications in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
Current Pharmaceutical Design The Evolving Therapy of Rheumatic Diseases, The Future is Now
Current Drug Targets - Immune, Endocrine & Metabolic Disorders Preventing and Treating Anthracycline-Related Cardiotoxicity in Survivors of Childhood Cancer
Current Cancer Therapy Reviews The Cardiac Conduction and Contractility Complications of Methamphetamine Use and the Relationship to Psychiatric Comorbidity: A Systematic Review
Current Psychiatry Research and Reviews Coenzyme Q10 in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases: Current State of the Problem
Current Cardiology Reviews Stiff Left Atrial Syndrome; Prospects and Possibilities. Retrospective Analysis and Review of the Literature
Current Hypertension Reviews