Abstract
The article entitled “miR-27b-3p Inhibits Invasion, Migration and Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition in Gastric Cancer by Targeting RUNX1 and Activation of the Hippo Signaling Pathway”, by Chen-Hui Bao and Lin Guo, has been retracted on the request of the Author in light of the changes to the University’s promotion policy, due to which the article needs further content.
Bentham Science apologizes to the readers of the journal for any inconvenience this may have caused.
Kindly see Bentham Science Policy on Article retraction at the link https://benthamscience.com/journals/anti-canceragents-in-medicinal-chemistry/editorial-policies/
Bentham Science Disclaimer: It is a condition of publication that manuscripts submitted to this journal have not been published and will not be simultaneously submitted or published elsewhere. Furthermore, any data, illustration, structure, or table that has been published elsewhere must be reported, and copyright permission for reproduction must be obtained. Plagiarism is strictly forbidden, and by submitting the article for publication the authors agree that the publishers have the legal right to take appropriate action against the authors if plagiarism or fabricated information is discovered. By submitting a manuscript, the authors agree that the copyright of their article is transferred to the publishers if and when the article is accepted for publication.
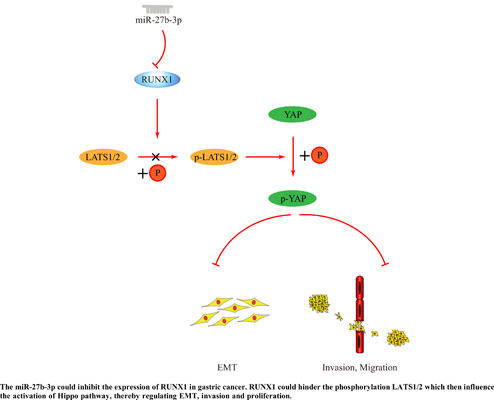
Keywords: miR-27b-3p, RUNX1, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, Hippo pathway, invasion, migration, gastric cancer.
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3322/caac.21338] [PMID: 26808342]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3322/caac.21590] [PMID: 31912902]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i8.2403] [PMID: 26937129]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010013] [PMID: 30577521]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i38.5773] [PMID: 31636471]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jso.23940] [PMID: 26175203]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0877-2] [PMID: 30154451]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2019.11.038] [PMID: 31811909]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2017.08.034] [PMID: 29074454]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.03.023] [PMID: 30951667]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1672-0229(08)60044-3] [PMID: 20172487]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6524-3_1] [PMID: 27826912]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2940-7] [PMID: 30374521]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9207-2_1] [PMID: 30963484]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236011] [PMID: 31795319]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2017.03.015] [PMID: 28322989]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27486] [PMID: 30471116]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051723] [PMID: 32138313]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.5114/wo.2014.47136] [PMID: 25691825]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.03.019] [PMID: 28356225]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/mc.22838] [PMID: 29749061]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1507] [PMID: 26704973]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41416-018-0109-7] [PMID: 29765148]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616] [PMID: 19910308]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv007] [PMID: 25605792]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/psp.2013.56] [PMID: 24132163]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.16409.1] [PMID: 30467523]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3233-2_22] [PMID: 28299668]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.03881] [PMID: 25415051]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2617-7] [PMID: 32487998]
[PMID: 31853285]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-1362-9] [PMID: 32561850]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1917969117] [PMID: 32482852]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314061] [PMID: 28866620]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2273-y] [PMID: 32041942]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-2168-y] [PMID: 31827075]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i17.2029] [PMID: 31114131]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4483] [PMID: 24782601]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12885-019-6163-6] [PMID: 31604467]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature25973] [PMID: 29489753]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2020.05.008] [PMID: 32577500]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10555-020-09905-7] [PMID: 32577859]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3892/ol.2020.11623] [PMID: 32565971]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2019.02.058] [PMID: 30849543]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082873] [PMID: 32326049]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.7150/thno.37621] [PMID: 32104496]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13046-015-0253-3] [PMID: 26576539]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1065-6995(03)00018-0] [PMID: 12788047]
[PMID: 31059069]
[PMID: 32024352]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3233-2_4] [PMID: 28299650]
[PMID: 31964134]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00418-018-1640-6] [PMID: 29356961]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117389] [PMID: 32007573]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1615/CritRevImmunol.2018025488] [PMID: 29717663]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.5483/BMBRep.2016.49.1.242] [PMID: 26592937]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20160632] [PMID: 28490659]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.88.23.10431] [PMID: 1720541]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-10-687830] [PMID: 28179279]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3233-2_26] [PMID: 28299672]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.274027.115] [PMID: 26728553]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2017.1323586] [PMID: 28532298]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00428-010-0986-5] [PMID: 20957493]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev-med-041217-010829] [PMID: 30691367]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010716-104846] [PMID: 27732800]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa126] [PMID: 32103257]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13312-020-1736-7] [PMID: 32060244]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.4155/fmc.15.107] [PMID: 26399457]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.13002] [PMID: 27816966]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1096/fj.201701533R] [PMID: 29505299]