Abstract
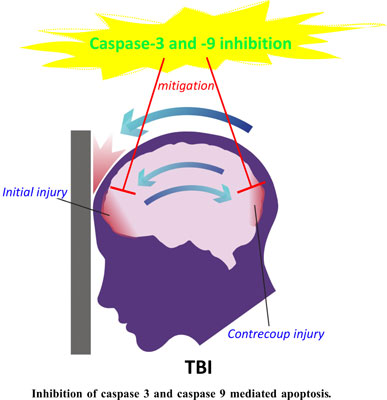
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is one of the significant causes of death and morbidity, and it is hence a focus of translational research. Apoptosis plays an essential part in the pathophysiology of TBI, and its inhibition may help overcome TBI's negative consequences and improve functional recovery. Although physiological neuronal death is necessary for appropriate embryologic development and adult cell turnover, it can also drive neurodegeneration. Caspases are principal mediators of cell death due to apoptosis and are critical for the required cleavage of intracellular proteins of cells committed to die. Caspase-3 is the major executioner Caspase of apoptosis and is regulated by a range of cellular components during physiological and pathological conditions. Activation of Caspase-3 causes proteolyzation of DNA repair proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, and the inhibitor of Caspase-activated DNase (ICAD) during programmed cell death, resulting in morphological alterations and DNA damage that define apoptosis. Caspase-9 is an additional crucial part of the intrinsic pathway, activated in response to several stimuli. Caspases can be altered post-translationally or by modulatory elements interacting with the zymogenic or active form of a Caspase, preventing their activation. The necessity of Caspase-9 and -3 in diverse apoptotic situations suggests that mammalian cells have at least four distinct apoptotic pathways. Continued investigation of these processes is anticipated to disclose new Caspase regulatory mechanisms with consequences far beyond apoptotic cell death control. The present review discusses various Caspase-dependent apoptotic pathways and the treatment strategies to inhibit the Caspases potentially.
Keywords: Traumatic brain injury, apoptosis, caspase-3, caspase-9, caspase-dependent apoptosis, caspase inhibitors.
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09541-4] [PMID: 31563989]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30371-X] [PMID: 29122524]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3816-2_27] [PMID: 27604735]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2015.10.002] [PMID: 26519659]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2015.03.007]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.12.005] [PMID: 26725141]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3233/JAD-143207] [PMID: 26401777]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.2217/nmt-2016-0017] [PMID: 27599555]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/13854046.2016.1257069] [PMID: 27855547]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13311-020-00840-7] [PMID: 32056100]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00528] [PMID: 31827423]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0165-5728(01)00409-X] [PMID: 11730942]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12028-009-9328-3] [PMID: 20087688]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000020922] [PMID: 32590803]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0121739] [PMID: 25822281]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/neu.2008.0657] [PMID: 19206997]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nurt.2009.10.019] [PMID: 20129502]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/cns.12127] [PMID: 23710877]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0166-2236(99)01479-4] [PMID: 10631785]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/nbdi.2002.0549] [PMID: 12505426]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jnen/nlv001] [PMID: 26671985]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/neu.2014.3741] [PMID: 25621407]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3233/JAD-140984] [PMID: 25171717]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.701301] [PMID: 34305609]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c140057] [PMID: 26140712]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.2002.00975.x] [PMID: 12091479]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S277457] [PMID: 33116753]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0711800105] [PMID: 18238895]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4400476] [PMID: 10200555]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1101620] [PMID: 22246630]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4402038] [PMID: 16977329]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1167/iovs.11-7570] [PMID: 21969293]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2017.44] [PMID: 28690332]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010814-124414] [PMID: 25340928]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.33.23426] [PMID: 10438520]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.040] [PMID: 32298652]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1348-0421.12756] [PMID: 31687791]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2009.09.013] [PMID: 19782763]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.1063703] [PMID: 12654726]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/713803693] [PMID: 11185963]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2014.03.005] [PMID: 24856110]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2121-14-32] [PMID: 23834359]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi100968m] [PMID: 20795673]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.241358198] [PMID: 11717445]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13578-019-0292-0] [PMID: 30962873]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/srep45126] [PMID: 28345580]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01895] [PMID: 32973786]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1247-0] [PMID: 27142195]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1196/annals.1299.032] [PMID: 15033718]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4402026] [PMID: 16977333]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115575] [PMID: 34070382]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1096/fj.02-1067fje] [PMID: 12738800]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/08977150260337967] [PMID: 12427325]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3639.2000.tb00262.x] [PMID: 10764048]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-09-03504.2002] [PMID: 11978827]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M105102200] [PMID: 11583996]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.231465798] [PMID: 11734640]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(03)00051-0] [PMID: 12620239]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/34214] [PMID: 9422513]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01926230701320337] [PMID: 17562483]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a008672] [PMID: 23732469]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1242/jcs.073643] [PMID: 20844150]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.02.013] [PMID: 22406265]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036002] [PMID: 22629307]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a008656]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.8.4386] [PMID: 9539746]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81477-4] [PMID: 9708736]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/384368a0] [PMID: 8934524]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7254.2007.00588.x] [PMID: 17588343]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.275.21.16007] [PMID: 10821855]
[PMID: 12528311]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/0929867023370761] [PMID: 11945133]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.740740.x] [PMID: 10646526]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/nbdi.2002.0521] [PMID: 12505417]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-391860-4.00013-6] [PMID: 22449930]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600338] [PMID: 16736044]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.01-05-0272] [PMID: 11907276]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00001756-200008210-00040] [PMID: 10976968]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1084/jem.20031771] [PMID: 14970175]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)61427-4] [PMID: 10862606]
[PMID: 20032392]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600544] [PMID: 15650747]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00272-0] [PMID: 11257230]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.221580098] [PMID: 11752425]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M510863200] [PMID: 16339151]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncb1204] [PMID: 15580265]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.1663108] [PMID: 18708583]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200104008] [PMID: 11551979]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-475X.2009.00459.x] [PMID: 19320891]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2004.10.012] [PMID: 15623433]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijc.10832] [PMID: 12516089]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3507-06.2006] [PMID: 17093075]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0014-2999(01)01489-3] [PMID: 11755132]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.10.048] [PMID: 17150209]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.08.017] [PMID: 19666005]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.WCB.0000138664.17682.32] [PMID: 15529012]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3171/spi.2005.3.1.0053] [PMID: 16122023]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.30.18530] [PMID: 9228015]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07330.x] [PMID: 19788417]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncb1005] [PMID: 12792650]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2007.03.019] [PMID: 17466630]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2008.10.014] [PMID: 19081073]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06751.x] [PMID: 19016842]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.06.009] [PMID: 19586613]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.177.4.2441] [PMID: 16888006]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/MCB.25.23.10543-10555.2005] [PMID: 16287866]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M414325200] [PMID: 15703181]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M802846200] [PMID: 18467326]
[PMID: 11912135]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a008730] [PMID: 23378585]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00077-5] [PMID: 11007473]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvi029] [PMID: 15749826]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35065125] [PMID: 11242052]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.5.998] [PMID: 11230124]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.7400795] [PMID: 17016456]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(03)00054-6] [PMID: 12620238]