Abstract
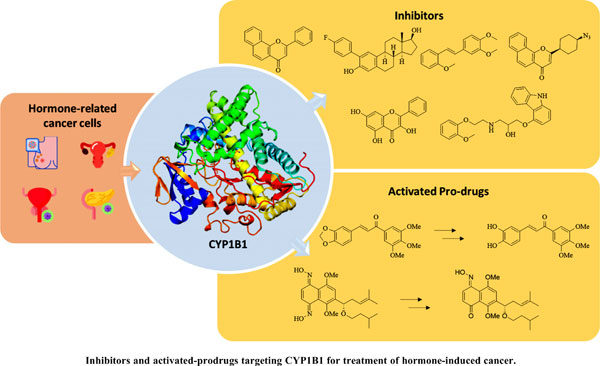
CYP1B1 plays an essential role in cancer's pathogenesis since it activates procarcinogens. Significantly, this enzyme catalyzes the hydroxylation of 17β-estradiol, leading to carcinogenic metabolites involved in carcinogenesis and cancer progression. Therefore, the inhibition of CYP1B1 activity is considered a therapeutic target for chemotherapy. In addition, CYP1B1 is overexpressed in hormone-dependent cancer cells and could be related to resistance to anticancer drugs. However, the activity of CYP1B1 in the tumor microenvironment can metabolize and activate prodrugs in cancer cells, providing more selectivity and being useful for chemoprevention or chemotherapy strategies. Furthermore, due to its importance in anticancer drug design, recent studies have reported using computational methods to understand the intermolecular interactions between possible ligands and CYP1B1. Therefore, in this perspective, we highlight recent findings in developing CYP1B1 inhibitors (flavonoids, trans-stilbenes, estradiol derivatives, and carbazoles) and CYP1B1-activated prodrugs (a chalcone DMU-135 and an oxime DMAKO-20). Finally, we have analyzed their possible molecular interactions with this enzymatic target by molecular docking, which can help to design new active substances.
Keywords: CYP1B1, cancer, CYP1A2, CYP1A1, ANF, cancer's pathogenesis.
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.8b00409] [PMID: 30613334]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1087057116675315] [PMID: 28139960]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/pr9050817]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2014.2041] [PMID: 25516145]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.10.013] [PMID: 29197745]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx980090+] [PMID: 9760279]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.204420] [PMID: 21147782]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.452953] [PMID: 23508959]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M611692200] [PMID: 17311915]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c3md00317e]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx100286d] [PMID: 21053930]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00907] [PMID: 30216063]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2018.11.045] [PMID: 30553624]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm2010332] [PMID: 22239221]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/cbdd.13042] [PMID: 28632937]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112235] [PMID: 32203789]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10637-006-5947-0] [PMID: 16505954]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b01062] [PMID: 30481041]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.07.012] [PMID: 25127868]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201402224] [PMID: 25234005]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jps.23765] [PMID: 24186380]
[http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/1568009620666201116112937] [PMID: 33200710]