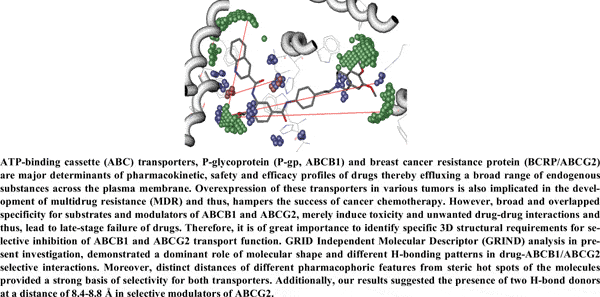
[1]
Szakacs, G.; Paterson, J.K.; Ludwig, J.A.; Booth-Genthe, C.; Gottesman, M.M. Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov., 2006, 5(3), 219-234.
[2]
Gottesman, M.M. Mechanisms of cancer drug resistance. Annu. Rev. Med., 2002, 53(1), 615-627.
[3]
(a)Jonker, J.W.; Smit, J.W.; Brinkhuis, R.F.; Maliepaard, M.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H.; Schinkel, A.H. Role of breast cancer resistance protein in the bioavailability and fetal penetration of topotecan. J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 2000, 92(20), 1651-1656.
(b)Kruijtzer, C.M.; Beijnen, J.H.; Rosing, H.; ten Bokkel Huinink, W.W.; Schot, M.; Jewell, R.C.; Paul, E.M.; Schellens, J.H. Increased oral bioavailability of topotecan in combination with the breast cancer resistance protein and P-glycoprotein inhibitor GF120918. J. Clin. Oncol., 2002, 20(13), 2943-2950.
[4]
(a)Stewart, C.F.; Leggas, M.; Schuetz, J.D.; Panetta, J.C.; Cheshire, P.J.; Peterson, J.; Daw, N.; Jenkins, J.J., III; Gilbertson, R.; Germain, G.S.; Harwood, F.C.; Houghton, P.J. Gefitinib enhances the antitumor activity and oral bioavailability of irinotecan in mice. Cancer Res., 2004, 64(20), 7491-7499.
(b) Breedveld, P.; Pluim, D.; Cipriani, G.; Wielinga, P.; van Tellingen, O.; Schinkel, A.H.; Schellens, J.H. The effect of Bcrp1 (Abcg2) on the in vivo pharmacokinetics and brain penetration of imatinib mesylate (Gleevec): implications for the use of breast cancer resistance protein and P-glycoprotein inhibitors to enable the brain penetration of imatinib in patients. Cancer Res., 2005, 65(7), 2577-2582.
(c) Elmeliegy, M.A.; Carcaboso, A.M.; Tagen, M.; Bai, F.; Stewart, C.F. Role of ATP-binding cassette and solute carrier transporters in erlotinib CNS penetration and intracellular accumulation. Clin. Cancer Res., 2011, 17(1), 89-99.
[5]
(a) Wattel, E.; Solary, E.; Hecquet, B.; Caillot, D.; Ifrah, N.; Brion, A.; Milpied, N.; Janvier, M.; Guerci, A.; Rochant, H.; Cordonnier, C.; Dreyfus, F.; Veil, A.; Hoang-Ngoc, L.; Stoppa, A.M.; Gratecos, N.; Sadoun, A.; Tilly, H.; Brice, P.; Lioure, B.; Desablens, B.; Pignon, B.; Abgrall, J.P.; Leporrier, M.; Fenaux, P. Quinine improves results of intensive chemotherapy (IC) in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) expressing P-glycoprotein (PGP). Updated results of a randomized study. Groupe Francais des Myelodysplasies (GFM) and Groupe GOELAMS. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 1999, 457, 35-46.
(b) Minderman, H.; O’Loughlin, K.L.; Pendyala, L.; Baer, M.R. VX-710 (biricodar) increases drug retention and enhances chemosensitivity in resistant cells overexpressing P-glycoprotein, multidrug resistance protein, and breast cancer resistance protein. Clin. Cancer Res., 2004, 10(5), 1826-1834.
(c) Pusztai, L.; Wagner, P.; Ibrahim, N.; Rivera, E.; Theriault, R.; Booser, D.; Symmans, F.W.; Wong, F.; Blumenschein, G.; Fleming, D.R.; Rouzier, R.; Boniface, G.; Hortobagyi, G.N. Phase II study of tariquidar, a selective P-glycoprotein inhibitor, in patients with chemotherapy-resistant, advanced breast carcinoma. Cancer, 2005, 104(4), 682-691.
[6]
von Richter, O.; Burk, O.; Fromm, M.F.; Thon, K.P.; Eichelbaum, M.; Kivisto, K.T. Cytochrome P450 3A4 and P-glycoprotein expression in human small intestinal enterocytes and hepatocytes: a comparative analysis in paired tissue specimens. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 2004, 75(3), 172-183.
[7]
Hoffmaster, K.A.; Turncliff, R.Z.; LeCluyse, E.L.; Kim, R.B.; Meier, P.J.; Brouwer, K.L. P-glycoprotein expression, localization, and function in sandwich-cultured primary rat and human hepatocytes: relevance to the hepatobiliary disposition of a model opioid peptide. Pharm. Res., 2004, 21(7), 1294-1302.
[8]
Karssen, A.M.; Meijer, O.; Pons, D.; De Kloet, E.R. Localization of mRNA expression of P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier and in the hippocampus. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 2004, 1032, 308-311.
[9]
Molsa, M.; Heikkinen, T.; Hakkola, J.; Hakala, K.; Wallerman, O.; Wadelius, M.; Wadelius, C.; Laine, K. Functional role of P-glycoprotein in the human blood-placental barrier. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 2005, 78(2), 123-131.
[10]
(a) Linton, K.J. Structure and function of ABC transporters. Physiology (Bethesda), 2007, 22, 122-130.
(b) Hill, C.R.; Jamieson, D.; Thomas, H.D.; Brown, C.D.; Boddy, A.V.; Veal, G.J. Characterisation of the roles of ABCB1, ABCC1, ABCC2 and ABCG2 in the transport and pharmacokinetics of actinomycin D in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. Pharmacol., 2013, 85(1), 29-37.
(c) Hu, M.; To, K.K.; Mak, V.W.; Tomlinson, B. The ABCG2 transporter and its relations with the pharmacokinetics, drug interaction and lipid-lowering effects of statins. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol., 2011, 7(1), 49-62.
dHu, M.; Tomlinson, B. Evaluation of the pharmacokinetics and drug interactions of the two recently developed statins, rosuvastatin and pitavastatin. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol., 2014, 10(1), 51-65.
[11]
(a) van Waterschoot, R.A.; ter Heine, R.; Wagenaar, E.; van der Kruijssen, C.M.; Rooswinkel, R.W.; Huitema, A.D.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schinkel, A.H. Effects of cytochrome P450 3A (CYP3A) and the drug transporters P-glycoprotein (MDR1/ABCB1) and MRP2 (ABCC2) on the pharmacokinetics of lopinavir. Br. J. Pharmacol., 2010, 160(5), 1224-1233.
(b) Windisch, A.; Timin, E.; Schwarz, T.; Stork-Riedler, D.; Erker, T.; Ecker, G.; Hering, S. Trapping and dissociation of propafenone derivatives in HERG channels. Br. J. Pharmacol., 2011, 162(7), 1542-1552.
(c) Zhang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Gong, Q.; Makielski, J.C.; January, C.T. Mechanism of block and identification of the verapamil binding domain to HERG potassium channels. Circ. Res., 1999, 84(9), 989-998.
[12]
(a) Li, J.; Jaimes, K.F.; Aller, S.G. Refined structures of mouse P-glycoprotein. Protein Sci., 2014, 23(1), 34-46.
(b) Szewczyk, P.; Tao, H.; McGrath, A.P.; Villaluz, M.; Rees, S.D.; Lee, S.C.; Doshi, R.; Urbatsch, I.L.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, G. Snapshots of ligand entry, malleable binding and induced helical movement in P-glycoprotein. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr., 2015, 7(Pt 3), 732-741.
[13]
Demel, M.A.; Schwaha, R.; Kramer, O.; Ettmayer, P.; Haaksma, E.E.; Ecker, G.F. In silico prediction of substrate properties for ABC-multidrug transporters. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol., 2008, 4(9), 1167-1180.
[14]
(a) Allen, J.D.; van Loevezijn, A.; Lakhai, J.M.; van der Valk, M.; van Tellingen, O.; Reid, G.; Schellens, J.H.; Koomen, G-J.; Schinkel, A.H. Potent and specific inhibition of the breast cancer resistance protein multidrug transporter in vitro and in mouse intestine by a novel analogue of fumitremorgin C 1 this work was supported in part by grant NKI 97-1433 from the Dutch Cancer Society (to AHS). Synthesis investigations by A. v. L. and GJ. K. were supported by the Netherlands Research Council for Chemical Sciences (NWO/CW) and the Netherlands Technology Foundation (STW). 1. Mol. Cancer Ther., 2002, 1(6), 417-425.
(b) Boumendjel, A.; Macalou, S.; Valdameri, G.; Pozza, A.; Gauthier, C.; Arnaud, O.; Nicolle, E.; Magnard, S.; Falson, P.; Terreux, R.; Carrupt, P.A.; Payen, L.; Di Pietro, A. Targeting the multidrug ABCG2 transporter with flavonoidic inhibitors: in vitro optimization and in vivo validation. Curr. Med. Chem., 2011, 18(22), 3387-3401.
(c) Fox, E.; Bates, S.E. Tariquidar (XR9576): a P-glycoprotein drug efflux pump inhibitor. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther., 2007, 7(4), 447-459.
[15]
Pastor, M.; Cruciani, G.; McLay, I.; Pickett, S.; Clementi, S. GRid-INdependent descriptors (GRIND): a novel class of alignment-independent three-dimensional molecular descriptors. J. Med. Chem., 2000, 43(17), 3233-3243.
[16]
Duran, A.; Martinez, G.C.; Pastor, M. Development and validation of AMANDA, a new algorithm for selecting highly relevant regions in Molecular Interaction Fields. J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2008, 48(9), 1813-1823.
[17]
Jabeen, I.; Wetwitayaklung, P.; Klepsch, F.; Parveen, Z.; Chiba, P.; Ecker, G.F. Probing the stereoselectivity of P-glycoprotein-synthesis, biological activity and ligand docking studies of a set of enantiopure benzopyrano[3,4-b][1,4]oxazines. Chem. Commun. (Camb.), 2011, 47(9), 2586-2588.
[18]
Magrane, M.; Consortium, U. UniProt Knowledgebase: a hub of integrated protein data. Database (Oxford), 2011, 2011, bar009..
[19]
Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Soding, J.; Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol., 2011, 7, 539.
[20]
Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2--a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(9), 1189-1191.
[21]
Aller, S.G.; Yu, J.; Ward, A.; Weng, Y.; Chittaboina, S.; Zhuo, R.; Harrell, P.M.; Trinh, Y.T.; Zhang, Q.; Urbatsch, I.L. Structure of P-glycoprotein reveals a molecular basis for poly-specific drug binding. Science, 2009, 323(5922), 1718-1722.
[22]
Shen, M.Y.; Sali, A. Statistical potential for assessment and prediction of protein structures. Protein Sci., 2006, 15(11), 2507-2254.
[23]
Colovos, C.; Yeates, T.O. Verification of protein structures: patterns of nonbonded atomic interactions. Protein Sci., 1993, 2(9), 1511-1519.
[24]
Lovell, S.C.; Davis, I.W.; Arendall, W.B., III; de Bakker, P.I.; Word, J.M.; Prisant, M.G.; Richardson, J.S.; Richardson, D.C. Structure validation by Calpha geometry: phi, psi and Cbeta deviation. Proteins, 2003, 50(3), 437-450.
[25]
Jones, G.; Willett, P.; Glen, R.C. Molecular recognition of receptor sites using a genetic algorithm with a description of desolvation. J. Mol. Biol., 1995, 245(1), 43-53.
[26]
Rosenberg, M.F.; Velarde, G.; Ford, R.C.; Martin, C.; Berridge, G.; Kerr, I.D.; Callaghan, R.; Schmidlin, A.; Wooding, C.; Linton, K.J. Repacking of the transmembrane domains of P‐glycoprotein during the transport ATPase cycle. EMBO J., 2001, 20(20), 5615-5625.
[27]
(a)Cramer, J.; Kopp, S.; Bates, S.E.; Chiba, P.; Ecker, G.F. Multispecificity of drug transporters: probing inhibitor selectivity for the human drug efflux transporters ABCB1 and ABCG2. ChemMedChem, 2007, 2(12), 1783-1788.
(b)Kühnle, M.; Egger, M.; Müller, C.; Mahringer, A.; Bernhardt, G.n.; Fricker, G.; König, B.; Buschauer, A. Potent and selective inhibitors of breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2) derived from the p-glycoprotein (ABCB1) modulator tariquidar. J. Med. Chem., 2009, 52(4), 1190-1197.
[28]
(a)Jabeen, I.; Pleban, K.; Rinner, U.; Chiba, P.; Ecker, G.F. Structure–activity relationships, ligand efficiency, and lipophilic efficiency profiles of benzophenone-type inhibitors of the multidrug transporter p-glycoprotein. J. Med. Chem., 2012, 55(7), 3261-3273.
(b)Klepsch, F.; Chiba, P.; Ecker, G.F. Exhaustive Sampling of Docking Poses Reveals Binding Hypotheses for Propafenone Type Inhibitors of P-Glycoprotein. PLOS Comput. Biol., 2011, 7(5), e1002036.
(c)Chiba, P.; Tell, B.; Jager, W.; Richter, E.; Hitzler, M.; Ecker, G. Studies on propafenone-type modulators of multidrug-resistance IV1): synthesis and pharmacological activity of 5-hydroxy and 5-benzyloxy derivatives. Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim), 1997, 330(11), 343-347.
[29]
Chang, C.; Ekins, S.; Bahadduri, P.; Swaan, P.W. Pharmacophore-based discovery of ligands for drug transporters. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 2006, 58(12-13), 1431-1450.
[30]
Rosenberg, M.F.; Bikadi, Z.; Chan, J.; Liu, X.; Ni, Z.; Cai, X.; Ford, R.C.; Mao, Q. The human breast cancer resistance protein
(BCRP/ABCG2) shows conformational changes with mitoxantrone. Structure (London, England : 1993),, 2010, 14(8), 482-493.
[31]
(a)Ecker, G.F.; Csaszar, E.; Kopp, S.; Plagens, B.; Holzer, W.; Ernst, W.; Chiba, P. Identification of ligand-binding regions of p-glycoprotein by activated-pharmacophore photoaffinity labeling and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization–time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Mol. Pharmacol., 2002, 61(3), 637-648.
(b)Pleban, K.; Kopp, S.; Csaszar, E.; Peer, M.; Hrebicek, T.; Rizzi, A.; Ecker, G.F.; Chiba, P. P-glycoprotein substrate binding domains are located at the transmembrane domain/transmembrane domain interfaces: a combined photoaffinity labeling-protein homology modeling approach. Mol. Pharmacol., 2005, 67(2), 365-374.
[32]
(a)Loo, T.W.; Clarke, D.M. Defining the drug-binding site in the human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein using a methan-ethiosulfonate analog of verapamil, MTS-verapamil. J. Biol. Chem., 2001, 276(18), 14972-14979.
(b)Loo, T.W.; Bartlett, M.C.; Clarke, D.M. Methanethiosulfonate derivatives of rhodamine and verapamil activate human P-glycoprotein at different sites. J. Biol. Chem., 2003, 278(50), 50136-50141.
[33]
Sareila, O.; Korhonen, R.; Kärpänniemi, O.; Nieminen, R.; Kankaanranta, H.; Moilanen, E. JAK inhibitors AG-490 and WHI-P154 decrease IFN-γ-induced iNOS expression and NO production in macrophages. Mediators Inflamm., 2006, 2006(2), 16161.
[34]
Bollag, G.; Hirth, P.; Tsai, J.; Zhang, J.; Ibrahim, P.N.; Cho, H.; Spevak, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Habets, G.; Burton, E.A.; Wong, B.; Tsang, G.; West, B.L.; Powell, B.; Shellooe, R.; Marimuthu, A.; Nguyen, H.; Zhang, K.Y.; Artis, D.R.; Schlessinger, J.; Su, F.; Higgins, B.; Iyer, R.; D’Andrea, K.; Koehler, A.; Stumm, M.; Lin, P.S.; Lee, R.J.; Grippo, J.; Puzanov, I.; Kim, K.B.; Ribas, A.; McArthur, G.A.; Sosman, J.A.; Chapman, P.B.; Flaherty, K.T.; Xu, X.; Nathanson, K.L.; Nolop, K. Clinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor needs broad target blockade in BRAF-mutant melanoma. Nature, 2010, 467(7315), 596-599.
[35]
(a)Vispute, S.G.; Cheng, J.; Sun, Y.; Sodani, K.S.; Singh, S.; Pan, Y.; Talele, T.; Ashby, C.R., Jr; Chen, Z. Vemurafenib (PLX4032, Zelboraf ®), a BRAF inhibitor, modulates ABCB1-, ABCG2-, and ABCC10-mediated multidrug resistance. J. Cancer Res. Updates, 2013, 2, 11.
(b)Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.K.; Wang, Y.J.; Kathawala, R.J.; Patel, A.; Zhu, H.; Sodani, K.; Talele, T.T.; Ambudkar, S.V.; Chen, Z.S.; Fu, L.W. WHI-P154 enhances the chemotherapeutic effect of anticancer agents in ABCG2-overexpressing cells. Cancer Sci., 2014, 105(8), 1071-1078.
[36]
Caron, G.; Ermondi, G. Influence of conformation on GRIND-based three-dimensional quantitative structure−activity relationship (3D-QSAR). J. Med. Chem., 2007, 50(20), 5039-5042.
[37]
Baroni, M.; Costantino, G.; Cruciani, G.; Riganelli, D.; Valigi, R.; Clementi, S. Generating optimal linear PLS estimations (GOLPE): an advanced chemometric tool for handling 3D-QSAR problems. Mol. Inform., 1993, 12(1), 9-20.
[38]
Jabeen, I.; Wetwitayaklung, P.; Chiba, P.; Pastor, M.; Ecker, G.F. 2D- and 3D-QSAR studies of a series of benzopyranes and benzopyrano[3,4b][1,4]-oxazines as inhibitors of the multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des., 2013, 27(2), 161-171.
[39]
Crivori, P.; Reinach, B.; Pezzetta, D.; Poggesi, I. Computational models for identifying potential P-glycoprotein substrates and inhibitors. Mol. Pharm., 2006, 3(1), 33-44.
[40]
Broccatelli, F.; Carosati, E.; Neri, A.; Frosini, M.; Goracci, L.; Oprea, T.I.; Cruciani, G. A Novel Approach for predicting p-glycoprotein (ABCB1) inhibition using molecular interaction fields. J. Med. Chem., 2011, 54(6), 1740-1751.
[41]
Boccard, J.; Bajot, F.; Di Pietro, A.; Rudaz, S.; Boumendjel, A.; Nicolle, E.; Carrupt, P.A. A 3D linear solvation energy model to quantify the affinity of flavonoid derivatives toward P-glycoprotein. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 2009, 36(2-3), 254-264.
[42]
Shukla, S.; Kouanda, A.; Silverton, L.; Talele, T.T.; Ambudkar, S.V. Pharmacophore modeling of nilotinib as an inhibitor of ATP-binding cassette drug transporters and BCR-ABL kinase using a three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship approach. Mol. Pharm., 2014, 11(7), 2313-2322.